The Best Ecommerce Site Structure for SEO

Today, you’ll learn about how to make the perfect ecommerce site structure for SEO success.
Here, we’ll go through 11 tips on creating an effective site structure that can be easily crawled by search engines like Google.
Let’s get into it:
What is an SEO Friendly Website Structure?
An SEO-friendly website structure includes organised content and a logical hierarchy. It uses internal links that help users navigate between pages, descriptive URLs, topic clusters that group relevant content together, and a clear site map.
While a seamless structure is important for all websites, it holds added value for Ecommerce brands. Users want to find the products they’re looking for and enjoy a speedy checkout process, as these statistics show:
- Ecommerce websites lose an estimated £1.4 billion worth of sales annually due to poor website experiences (Ecommerce Age).
- 88% of consumers are less likely to return to a website after a poor experience (Linearity).
60% of consumers abandon carts due to slow loading times and bad design elements (PR Newswire).
The Benefits of Having an Optimised Ecommerce Site Structure
A seamless Ecommerce website structure doesn’t just boost user experience; it also ensures that search engine crawlers can recognise and understand your content.
The result? Higher rankings, more sales, and a loyal network of customers:
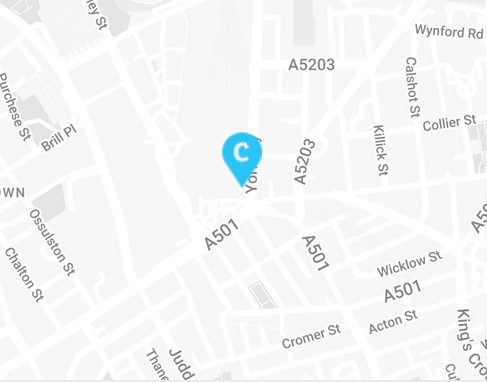
- – Crawlability: Search engines need to crawl and understand your website to rank it. Having a clear site structure makes it easier for the search engines to understand your content, index it, and rank the website accordingly.
- – Streamlined Navigation: We live in a busy world, and consumers want to access products without hassle. When your website’s navigation elements are on-point, it ensures that your target audience can find what they’re looking for.
- – Higher Engagement Rates: Websites with high bounce rates are less likely to secure high SERP rankings, but optimising the structure often means visitors stick around for longer.
- – Responsivity: Did you know that 59% of all Ecommerce sales come from a mobile device? If your website isn’t responsive across all devices, you’re losing out on potential sales, but optimising your site structure for mobile devices removes barriers to sales.
- – Organic Visibility: When your website pages and products are optimised for SEO and organised correctly, it enhances your chances of appearing in relevant searches.
- – Trust Signals: Gaining the trust of your target audience is essential for turning one-time purchases into loyal customers. When your website is professional with a seamless structure, it builds trust.
How to Structure an Ecommerce Site for SEO in 11 Steps
SEO isn’t just about finding some relevant keywords and inserting them into your content; it’s an intensive process.
Yes, on-page SEO is vital for appearing in relevant searches, but the behind the scenes elements (technical SEO) play a key role in ranking, organic traffic, and conversions.
Following our Ecommerce SEO checklist gives you the best chance of outranking your competitors and building a successful business.
1: Perform an SEO Audit
Before you even think about optimising your website, you should gain a clear understanding of its current structure and rankings. Performing an Ecommerce SEO audit gives you the opportunity to review what’s working and spot any critical errors, including:
- – Slow page loading times
- – Broken links
- – Crawl errors
- – UX flaws
Once you identify areas for improvement, you can create a list of priorities.
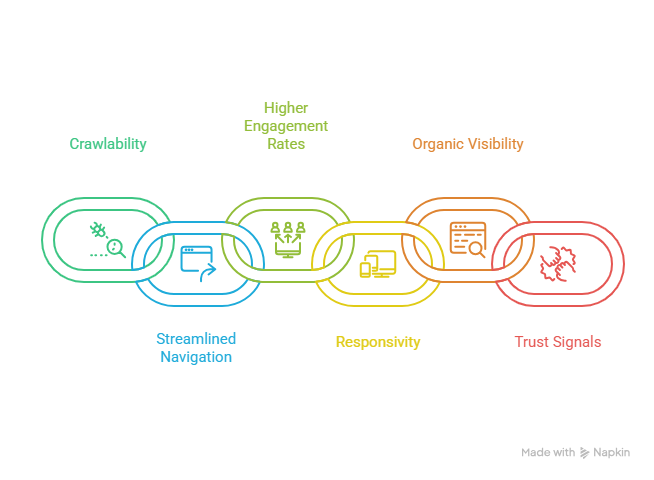
2: Follow the Three Levels Deep Rule
When it comes to Ecommerce site structure, SEO friendly websites follow the three-level deep rule.
This means that the user is never more than three clicks away from their intended destination, which improves the shopping experience and makes it easier for the search engines to rank your site.
As you can see from this navigational structure example, each level has a purpose:
3: Ecommerce URL Structure
URL structures are essential to SEO, as they’re the first thing crawlers see when they discover your web page. Your Ecommerce URL structures should be logical and accurately explain what the page is about. It should follow the hierarchical structure you have in place. For example, an Ecommerce URL example for a store selling trainers could be: domain.com/trainers/product.
4: Focus on Simplicity for Website Menus
The menu of your website is often one of the first places your visitors will go, and it should align with the hierarchical structure.
Simple menus with clear categories and pages ensure a smooth user experience. In contrast, convoluted menus with multiple links can make your visitors feel like they’re moving through a maze of content.
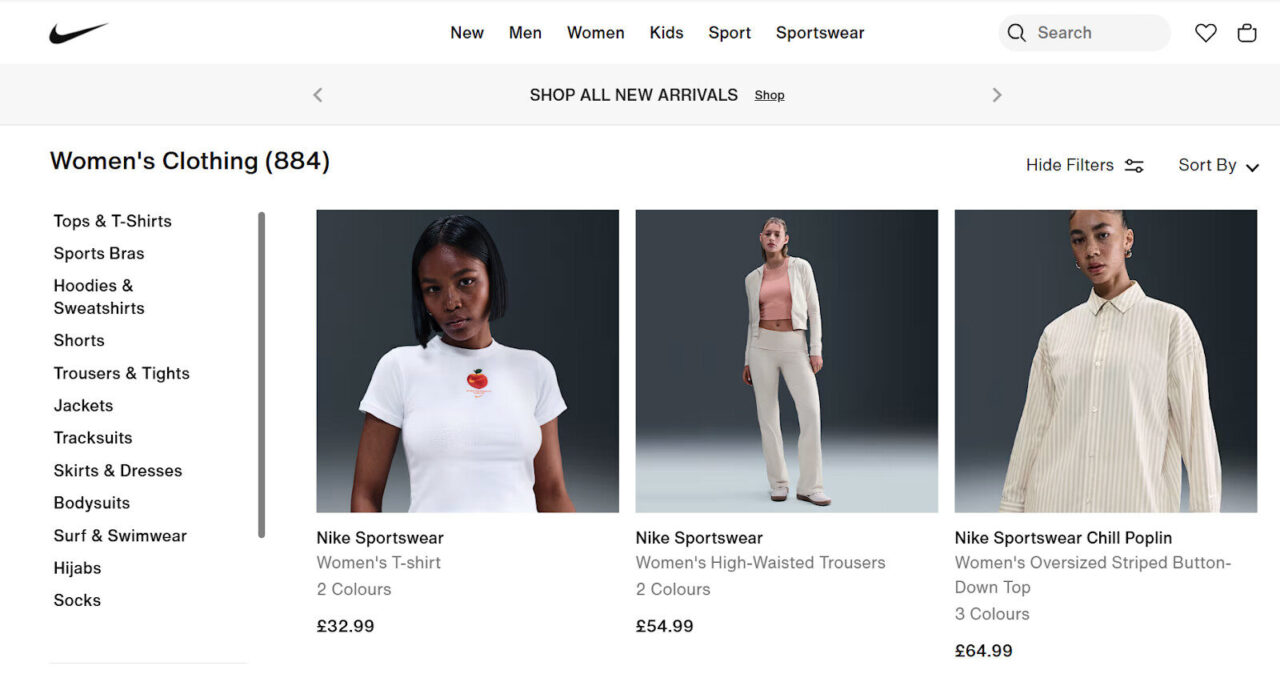
As many Ecommerce sites have a lot of categories and products, a common tactic is to deploy a side menu, as it makes it easier for users to find the products they’re looking for.
Nike is a perfect example of a professional side menu, and it lets users filter their search, instead of clicking on multiple pages to find a product.
5: Product and Category Page Optimisation
The next step in ensuring a seamless Ecommerce site structure is to optimise the category and product pages for visibility.
By taking the time to research keywords and analysing which terms your competitors are using, you can ensure that the search engines can find them and show them to audiences actively looking for your products.
Keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush and Ahrefs are excellent for finding relevant keywords, and they’ll also show you which terms your main competitors are targeting.
The general rule for optimising category and product pages is as follows:
- – Categories: Use plural terms and broad keywords such as women’s trainers and men’s formal shoes.
- – Products: Use specific keywords that match the product. For example, Nike Air Max (model number).
6: Ensure Mobile Responsivity
One of the most significant issues we frequently encounter with Ecommerce websites is their lack of mobile-friendly features. Your website could look amazing on desktop devices, but that doesn’t mean it will provide an amazing UX across mobile devices.
Every single page and product should load seamlessly on mobile devices and tablets, as many people shop on their mobiles.
Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means that Google takes the mobile version of a website as the primary source for ranking a page in search results.
Most SEO tools have free testing features that show you how your device appears across all devices, making it easy to identify issues and fix them.
7: Don’t Forget Header Tags
Header tags are essential components of on-page SEO, as they add structure to your content and make it easy for search engines and audiences to read. You can follow this simple rule when using header tags:
- – H1: The H1 tag is for the main heading of your page and it should always include the focus keyword. There should only be one main heading.
- – H2: H2s are top-level sub-headings that break the content into sections.
- – H3: When you want to go into more detail for each section, you can use H3s. H4, H5, and H6 tags enable you to split each point into further detail.
For example, on this very page, our “How to Structure an Ecommerce Site for SEO in 11 Steps” heading is an H2 tag, and all of these subsequent sections have H3 tags.
8: Use Breadcrumbs
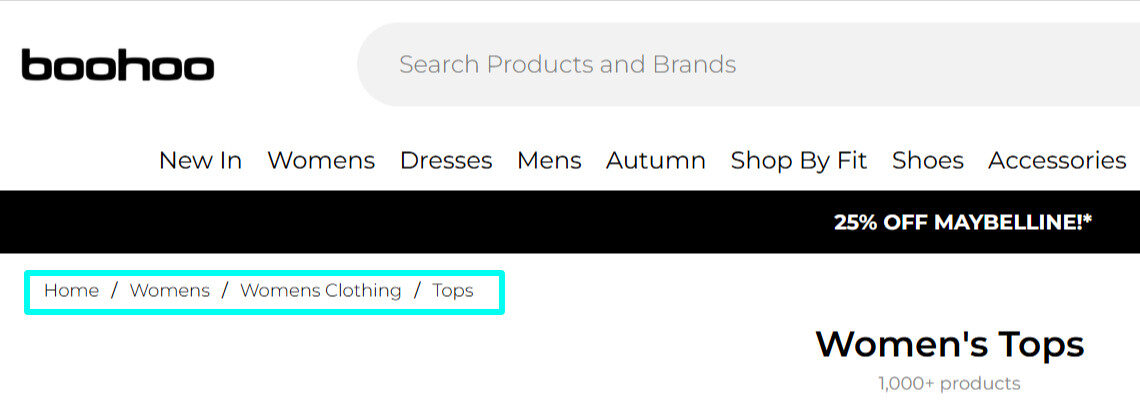
Breadcrumbs are essential Ecommerce SEO strategies, as they let users navigate from products back to the main categories and homepage.
Website visitors often want to browse through category pages and compare products before making a purchase – breadcrumbs make their journey a lot easier.
As a form of internal linking, they also improve your website’s rankings by assigning link equity to high-level pages and enabling search engines to index your site efficiently.
Boohoo is an excellent example of proper breadcrumb use, as visitors can easily navigate from women’s tops back to the main clothing category and homepage.
Top Tip: Instead of just implementing breadcrumbs on your website, use structured data to boost their chances of showing up in the SERPs.
9: Create a Structured Sitemap
Every Ecommerce website should have an XML sitemap, as it provides search engine crawlers with information about your main pages, categories, and products.
When the search engines understand your website, they’ll rank it more efficiently, which means that you can secure more organic visibility and website traffic.
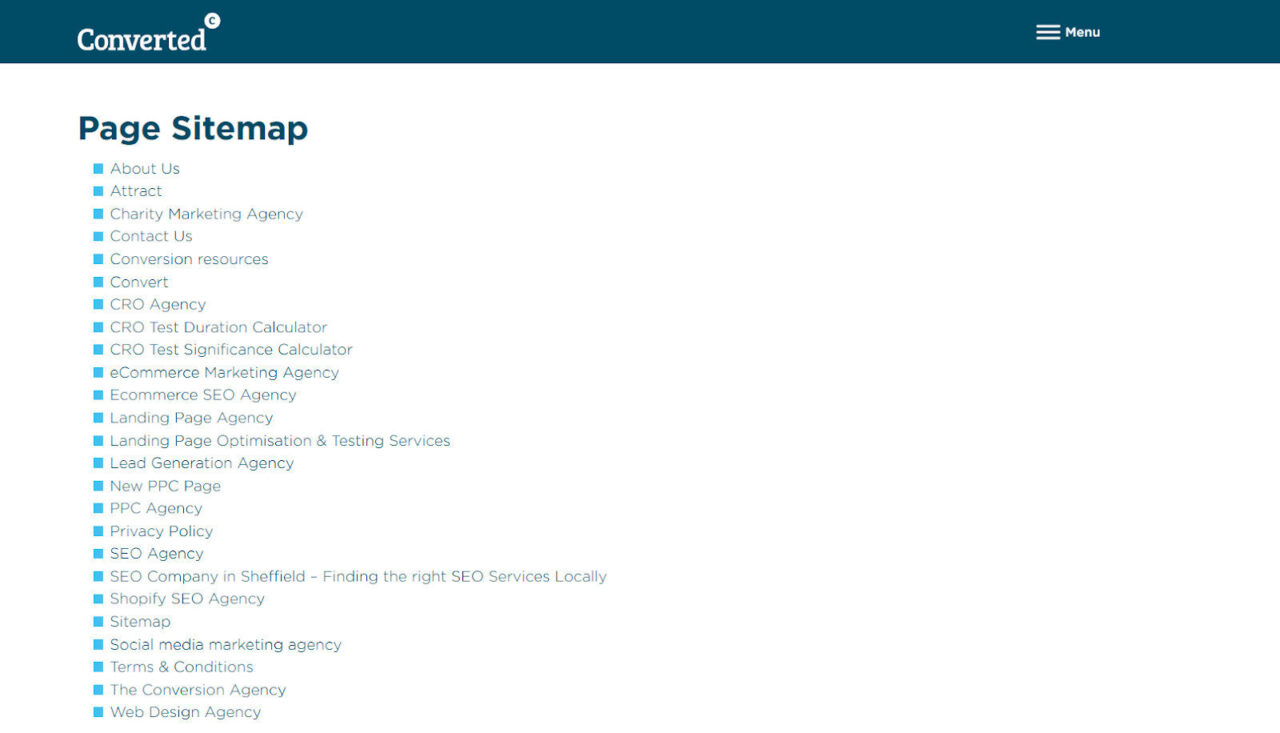
It’s always a good idea to submit your XML sitemap to Google Search Console and repeat the process when you make changes to the content. You could also create an HTML sitemap and add it to your footer to ensure that website visitors can find the pages they’re looking for, as you can see from the Converted sitemap:
10: Fix Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are pages that don’t have any internal links pointing towards them. Search engine crawlers use links to get around a website, which means orphan pages aren’t easily discovered and usually result in not being indexed.
You can find orphan pages using software like Screaming Frog, SEMrush, or Ahrefs.
As a good starting point, we’d recommend having at least 3 internal links pointing to every page.
11: Fix All Broken Links
We’ve covered internal links a lot in this post, but now it’s time to focus on broken links.
A broken link is a link that takes users to a page that isn’t working. Not only can this be frustrating for users, but it can also waste crawl budget sending crawlers to dud pages.
When both audiences and search engine bots land on broken links, it can make your website appear less reliable and lead to high bounce rates.
The most common example of a broken link is a 404 error, which displays on the web page when a user tries to access it. Tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, Ahrefs and Screaming Frog can help you find and fix these links.
How to Fix Broken Links on your Ecommerce Site
- – Remove Them: If your page is no longer in use, you can remove the internal links pointing towards the page, and then remove the page completely from the website with a 410 (Gone) HTTP status code.
- – Redirects: If your page still has SEO value (it has backlinks pointing towards it), you can redirect it to a new version or closely related page.
The Bottom Line
Implementing the Ecommerce SEO strategies in this guide can help you improve your organic visibility and boost your traffic, but they also give you the best chance of turning visitors into loyal customers.
Once you have the foundations nailed down, you can focus on creating compelling product descriptions and building a successful business.
Many online store owners wonder how to do SEO for an E-commerce website, and the process can be complex.
That’s why using a professional Ecommerce SEO agency can be beneficial, as you can focus on running your store and let the experts handle the on-page and technical optimisation.
If you’d like support, please feel free to contact us today for a free consultation.